Understanding BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) vs. Classic Bluetooth: A Comprehensive Guide
Bluetooth technology has evolved significantly, powering a wide range of devices from wireless headphones to smart home gadgets. Two key variants dominate the Bluetooth ecosystem: Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) and Classic Bluetooth (BT). In this article, we'll explore their differences, highlight BLE's power efficiency, discuss communication range, and provide insights into their development for Android applications.
I. Key Differences Between BLE and Classic Bluetooth
1.Power Consumption:
BLE: Designed for low power consumption, BLE is optimized for devices that need to run for months or even years on a single coin-cell battery. It achieves this through short, intermittent data bursts and a sleep-heavy operation mode.
Classic Bluetooth: Consumes more power, making it suitable for applications requiring continuous data streaming, such as audio playback or file transfers.
2.Data Transfer Rates:
BLE: Limited to small data packets (up to 20 bytes per transmission), ideal for applications like sensor data or IoT device communication.
Classic Bluetooth: Supports higher data rates, with traditional modules offering up to 3 Mbps and high-speed modules reaching up to 24 Mbps, perfect for music streaming or voice calls.
3.Compatibility:
BLE: Not backward compatible with Classic Bluetooth. Devices must support BLE (Bluetooth 4.0 or higher) to communicate.
Dual-Mode Devices: Branded as Bluetooth Smart Ready, these devices support both BLE and Classic Bluetooth, enabling compatibility across a broader range of devices.
4.Use Cases:
BLE: Powers IoT devices like smartwatches, fitness trackers, and smart home sensors due to its low power requirements and ability to handle small, periodic data transfers.
Classic Bluetooth: Commonly used for high-bandwidth applications like wireless speakers, headsets, and file transfers.
5.Power Classes (Classic Bluetooth):
Classic Bluetooth has three power classes:
Class 1: Up to 100 meters range.
Class 2: Up to 10 meters range.
Class 3: Up to 1 meter range.
II. BLE's Power Efficiency Advantages
BLE's low power consumption is its hallmark, making it a cornerstone of modern IoT ecosystems. Here's how it achieves this:
Sleep Mode: BLE devices spend most of their time in a low-power sleep state, waking up only to send or receive small data packets.
Short Connection Times: BLE uses quick, intermittent connections to transmit data, minimizing active time.
Efficient Protocol: Based on the GATT (Generic Attribute Profile) protocol, BLE transmits small data payloads, reducing energy use compared to Classic Bluetooth's continuous streaming.
Optimized for Small Data: BLE is designed for applications like heart rate monitors or temperature sensors, which send small, infrequent updates, further reducing power demands.
For example, a BLE-powered fitness tracker can operate for months on a single coin-cell battery, while a Classic Bluetooth headset may require frequent recharging due to its higher power demands.
III. BLE Communication Range
The communication range of BLE depends on several factors, including hardware, environment, and power settings:
1.Typical Range: BLE typically supports a range of 10–100 meters in open environments, similar to Classic Bluetooth Class 2 and Class 1.
2.Factors Affecting Range:
Antenna Design: Better antenna designs can extend range.
Environmental Interference: Walls, furniture, or other obstacles can reduce range.
Power Settings: Higher power settings can increase range but consume more energy.
3.Bluetooth 5.0 and Beyond: With Bluetooth 5.0, BLE introduced a long-range mode that can theoretically reach up to 1 km under ideal conditions, though real-world ranges are typically lower due to interference.
IV. BLE vs. Classic Bluetooth in Android Development
(I) BLE Development
BLE operates using the GATT protocol, which organizes data into Services, Characteristics, and Descriptors, each identified by a unique UUID. Here's a simplified workflow for Android BLE development (supported on Android 4.3 and above, with full Bluetooth 5.0 support from Android 8.0):
1.Obtain BluetoothAdapter:
BluetoothAdapter mBluetoothAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
2.Scan for Devices:
For Android 4.3–4.4:
BluetoothAdapter mBluetoothAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
For Android 5.0+:
BluetoothLeScanner mBluetoothLeScanner = mBluetoothAdapter.getBluetoothLeScanner(); mBluetoothLeScanner.startScan(mScanCallback);
3.Connect to a Device:
Use GATT to connect to a device, retrieve services, and interact with characteristics for reading, writing, or subscribing to notifications.
4.Read/Write Data:
BLE supports small data packets (up to 20 bytes). For larger data, split it into chunks:
if (data.length > 20) { for (int i = 0; i
5.Subscribe to Notifications:
Recently Posted
-
The KT148A Chip Gives Robot Vacuums a Voice for Worry-Free Whole-Home Cleaning
November 30, 2025In recent years, as living standards improve and work pressure increases, more and more households have begun relying on smart app Read More
Read More -
Application of KT148A Voice Chip in Smart Infusion Monitoring Systems
September 25, 2025Introduction: When Medical Devices Meet Intelligent Voice PromptsIn modern medical environments, infusion therapy is a common trea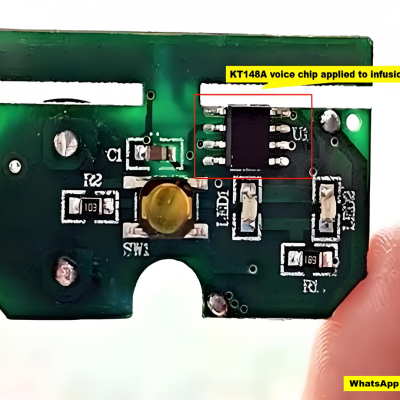 Read More
Read More -
KT142A - 16S MP3 Decoding Chip: Unleashing a New Intelligent Experience for Children's Electric Toot
September 16, 2025"Brushing teeth is like a battle!" This is the helpless feeling of many parents. Surveys show that over 70% of children Read More
Read More -
Introduction to AC6951C Bluetooth Transmitter and Receiver Module
September 9, 2025I. Product Picture II. Peripheral Function DescriptionThe following is the functional description corresponding to each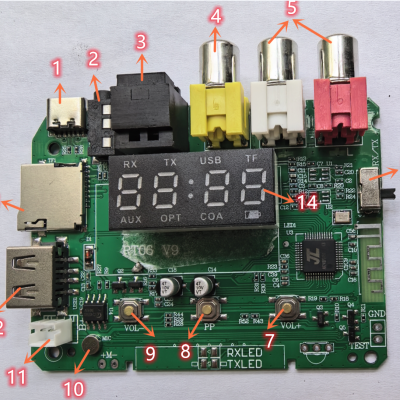 Read More
Read More